In the realm of combat and protection, shields have stood as unwavering guardians, safeguarding warriors from harm. Their construction, a testament to human ingenuity, has evolved over millennia, with each era leaving its unique mark on the art of shield-making.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the fascinating history, intricate components, and diverse variations of shield recipes, empowering you to craft impenetrable defenses for any battle or purpose.
From ancient warriors clad in bronze shields to modern soldiers wielding advanced composites, the shield has been an indispensable tool for survival. Its design and materials have been shaped by cultural beliefs, technological advancements, and the ever-changing nature of warfare.
Join us as we embark on a journey through the captivating world of shield recipes, unlocking the secrets to crafting shields that will withstand the test of time.
Shield Recipe History
The origins of shield recipes can be traced back to ancient times, when warriors sought to protect themselves from enemy attacks. The earliest known shield recipes were simple mixtures of natural materials, such as leather, wood, and animal hide.
Over time, shield recipes became more sophisticated, as new materials and techniques were developed. In the Middle Ages, for example, shields were often made of metal, such as iron or steel. These shields were more durable and could withstand more powerful blows than their predecessors.
Influence of Cultural Beliefs
The design and construction of shields has also been influenced by cultural beliefs. In some cultures, for example, shields were seen as symbols of power and authority. As a result, they were often decorated with elaborate designs and symbols.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have also played a role in the evolution of shield recipes. In the 19th century, for example, the invention of gunpowder led to the development of new types of shields that were designed to protect against bullets.
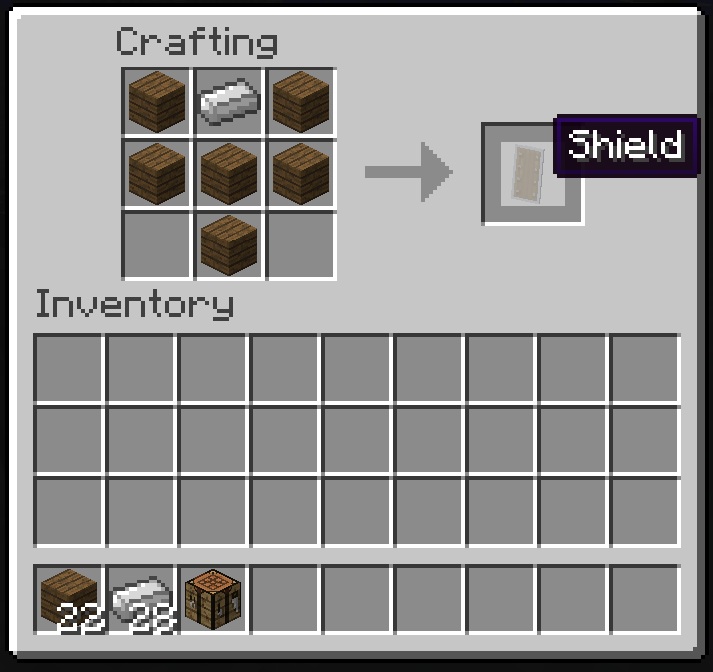
Shield Recipe Components
A shield recipe comprises various components, each serving specific functions and contributing to the shield’s overall performance and durability.
The essential components of a shield recipe include:
Materials
The choice of materials used in a shield recipe significantly impacts the shield’s properties and performance. Common materials include:
- Wood: Lightweight and resilient, wood provides a strong and durable base for shields.
- Metal: Plates of metal, such as iron or steel, offer superior protection against piercing and slashing attacks.
- Leather: Tough and flexible, leather is often used to cover the shield’s surface, providing additional protection and grip.
- Fabric: Layers of fabric, such as linen or canvas, can be used to reinforce the shield’s structure and absorb impact.
Shield Recipe Variations
The art of shield-making has seen a wealth of variations over time, each influenced by factors such as the availability of materials, the intended purpose of the shield, and regional preferences.
Variations in shield recipes can affect the shield’s durability, weight, and resistance to different types of attacks. For instance, a shield made with a thicker core of wood or metal will be more durable but heavier, while a shield with a thin core and a layer of leather or hide will be lighter and more flexible.
Shield Core Variations
The core of a shield provides the main structural support and determines its overall strength. Common materials for shield cores include wood, metal, and leather.
- Wood: Wooden cores are lightweight and easy to work with, making them a popular choice for shields of all types. However, wood can be susceptible to splitting and rot, especially in humid environments.
- Metal: Metal cores provide excellent protection against both blunt and sharp attacks. However, metal shields are heavier and more expensive to make.
- Leather: Leather cores are flexible and durable, making them well-suited for shields that need to be able to absorb impact without breaking.
Shield Facing Variations
The facing of a shield is the material that covers the front of the shield and provides protection against attacks. Common materials for shield facings include wood, metal, leather, and hide.
- Wood: Wooden facings are lightweight and easy to work with, but they are not as durable as metal facings.
- Metal: Metal facings provide excellent protection against both blunt and sharp attacks, but they are heavier and more expensive than wooden facings.
- Leather: Leather facings are flexible and durable, making them well-suited for shields that need to be able to absorb impact without breaking.
- Hide: Hide facings are similar to leather facings, but they are thicker and more durable.
Shield Binding Variations
The binding of a shield is the material that holds the core and facing together. Common materials for shield bindings include leather, rawhide, and metal.
- Leather: Leather bindings are flexible and durable, making them well-suited for shields of all types.
- Rawhide: Rawhide bindings are similar to leather bindings, but they are stronger and more resistant to moisture.
- Metal: Metal bindings provide excellent protection against both blunt and sharp attacks, but they are heavier and more expensive than leather or rawhide bindings.
Shield Recipe Design Considerations
Creating a shield requires careful consideration of various design aspects to ensure its effectiveness and functionality. These considerations include shape, size, weight, and durability, which are influenced by the intended use and available materials.
Shield shape is crucial as it affects its ability to deflect blows. Round shields offer excellent all-around protection, while rectangular shields provide better coverage for the torso. Triangular shields, on the other hand, are more maneuverable and suitable for close combat.
Shield Size
The size of the shield should be proportionate to the user’s height and strength. A shield that is too large may be cumbersome and difficult to handle, while one that is too small may not provide adequate protection. The ideal size allows the user to cover their body effectively without compromising mobility.
Shield Weight
Weight is a critical factor in shield design. A heavy shield can be tiring to carry and slow down the user. Conversely, a lightweight shield may not offer sufficient protection. The weight of the shield should be carefully balanced between durability and portability.
Shield Durability
The durability of a shield is determined by the materials used and the construction techniques. Wood, leather, and metal are common shield materials, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The shield should be able to withstand repeated blows without breaking or becoming ineffective.
Shield Recipe Manufacturing Techniques
Shield manufacturing encompasses a range of techniques, each tailored to the specific materials and design requirements. These techniques involve careful preparation of materials, shaping and forming, and final assembly.
Safety is paramount in shield manufacturing. Proper protective gear, such as gloves, safety glasses, and respirators, should be worn. Adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent inhalation of hazardous fumes or dust.
Material Preparation
The first step in shield manufacturing is material preparation. Common shield materials include wood, metal, leather, and composite materials. Wood is often used for lightweight shields, while metal provides superior protection against piercing and slashing attacks. Leather is flexible and durable, making it suitable for shields that require maneuverability.
Composite materials combine different materials to achieve specific properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratio.
Shield Recipe Performance Evaluation
Evaluating the performance of shield recipes is crucial to ensure they meet the intended design criteria and provide optimal protection. Performance evaluation involves assessing factors such as strength, durability, and resistance to impact.
Strength tests measure the shield’s ability to withstand static or dynamic loads. Common tests include tensile strength, compression strength, and flexural strength, which assess the shield’s resistance to pulling, crushing, and bending forces, respectively.
Durability Tests
Durability tests evaluate the shield’s ability to withstand repeated or prolonged exposure to environmental factors and wear and tear. These tests include:
- Environmental durability tests: Assess the shield’s resistance to extreme temperatures, moisture, UV radiation, and corrosive substances.
- Wear resistance tests: Determine the shield’s ability to withstand abrasion, impact, and repeated flexing without compromising its integrity.
Impact Resistance Tests
Impact resistance tests measure the shield’s ability to absorb and dissipate energy from impacts. These tests simulate real-world scenarios and include:
- Ballistic impact tests: Assess the shield’s resistance to high-velocity projectiles, such as bullets or shrapnel.
- Blunt impact tests: Evaluate the shield’s ability to withstand blunt force trauma, such as from falling objects or vehicle collisions.
Performance tests provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of shield recipes and help guide design decisions to optimize protection levels and ensure the safety of users.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the art of shield-making is a tapestry woven from history, science, and human resilience. By understanding the essential components, variations, and design considerations involved in shield recipes, we gain the power to create defenses that are both effective and aesthetically pleasing.
Whether for historical reenactment, cosplay, or simply as a testament to human ingenuity, the knowledge of shield recipes empowers us to safeguard ourselves and those we care for. As we continue to innovate and refine our techniques, the legacy of shield-making will endure, ensuring that the guardians of our future are well-equipped to face any challenge that may come their way.
Helpful Answers
What are the key components of a shield recipe?
The essential components of a shield recipe typically include a base material (wood, metal, or composite), a reinforcement material (leather, fabric, or fiberglass), and an adhesive to bind them together.
How do different materials affect the performance of a shield?
The choice of materials used in a shield recipe significantly influences its weight, durability, and resistance to impact. Heavier materials provide greater protection but can be more cumbersome, while lighter materials offer increased mobility but may compromise strength.
What are some common variations in shield recipes?
Shield recipes vary based on cultural influences, intended use, and available materials. Some variations include the use of different base materials (e.g., wood, metal, or composite), the addition of reinforcing layers (e.g., leather, fabric, or fiberglass), and the application of specialized coatings or treatments.
