Mes buffer, a widely used buffer system in scientific research, plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal conditions for biological processes. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of mes buffer, from its purpose and history to its preparation methods, properties, applications, and safety considerations.
By delving into the intricacies of mes buffer recipe, we aim to empower researchers with the knowledge and techniques necessary to effectively utilize this versatile buffer in their scientific endeavors.
In this guide, we will explore the essential ingredients and equipment required for preparing mes buffer, as well as the step-by-step procedures involved. We will discuss the physical and chemical properties of mes buffer, including its pH, temperature stability, and ionic strength.
Additionally, we will examine the diverse applications of mes buffer in various scientific fields, such as molecular biology, biochemistry, and cell culture.
Mes Buffer Recipe Overview

Mes buffer, also known as morpholinoethanesulfonic acid buffer, is a widely used buffer solution in biological research. It is a zwitterionic buffer, meaning it carries both positive and negative charges at physiological pH, making it ideal for maintaining a stable pH in a variety of experimental conditions.
Mes buffer was first developed in the 1970s as an alternative to other commonly used buffers, such as Tris and HEPES. It has since become a popular choice for cell culture, protein purification, and other biochemical applications due to its high buffering capacity, low toxicity, and minimal interference with biological systems.
Uses of Mes Buffer
Mes buffer is used in a wide range of biological applications, including:
- Cell culture: Mes buffer is commonly used to maintain a stable pH in cell culture media, supporting optimal cell growth and function.
- Protein purification: Mes buffer is often used in protein purification protocols to maintain a consistent pH during various purification steps, ensuring protein stability and activity.
- Biochemical assays: Mes buffer is employed in various biochemical assays, such as enzyme assays and protein-protein interaction studies, to maintain a controlled pH environment for accurate and reproducible results.
Ingredients and Equipment
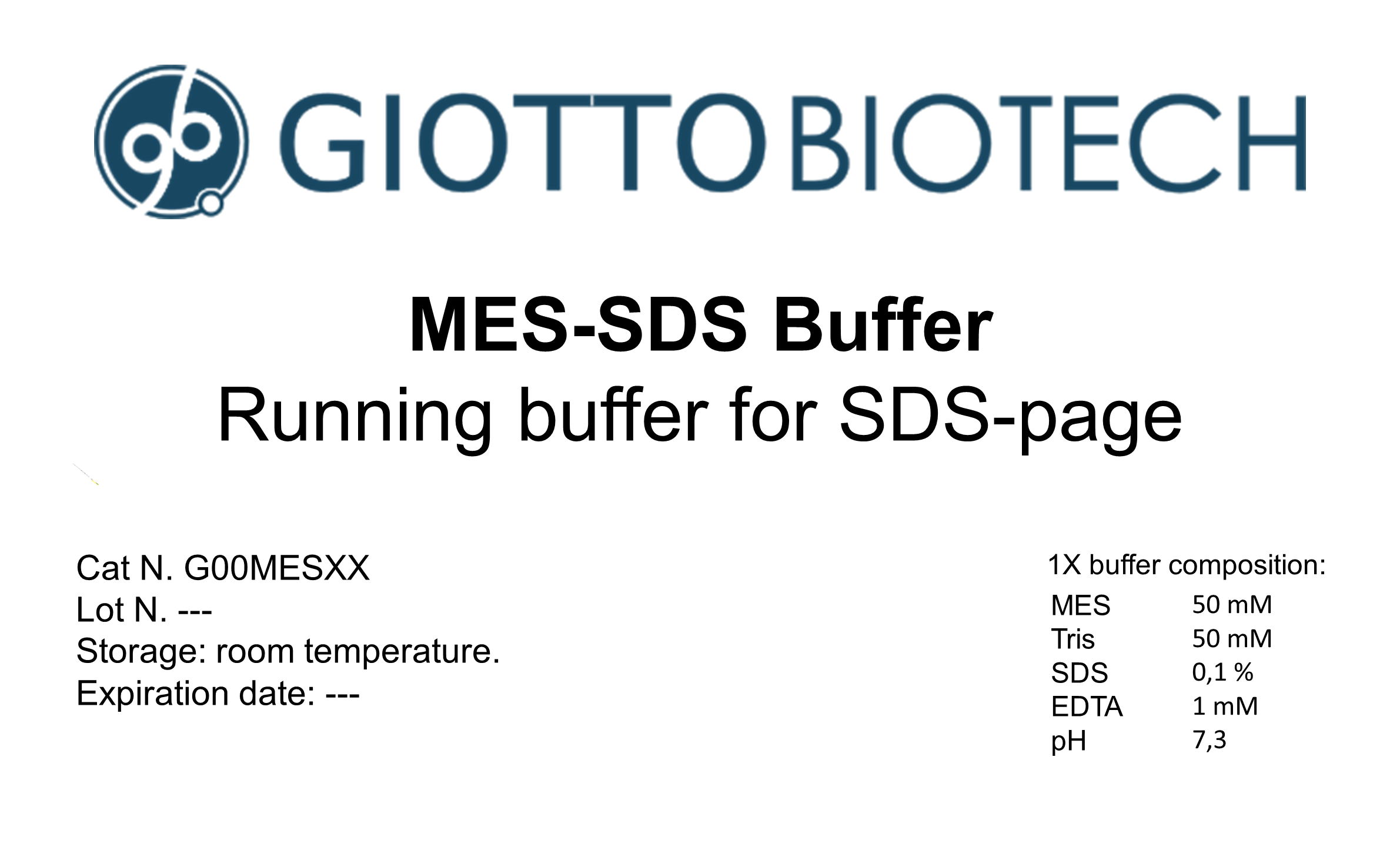
Preparing Mes buffer involves using specific ingredients and employing appropriate equipment. Understanding these components is crucial for successful buffer preparation.
The essential ingredients required for Mes buffer preparation include:
- Mes (2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Distilled water
Regarding equipment, the following items are necessary:
- pH meter or pH paper
- Graduated cylinder or pipette
- Magnetic stirrer or stir bar
- Glassware (e.g., beaker, flask)
Preparation Methods
Preparing MES buffer involves a simple and straightforward process that can be easily carried out in the laboratory. This buffer is commonly utilized in molecular biology applications, particularly in nucleic acid extraction and manipulation.
To prepare MES buffer, follow these steps:
Materials Required
- MES (2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid) powder
- Deionized water
- pH meter
- Magnetic stirrer
- Glassware (beaker, graduated cylinder, stir bar)
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Calculate the required amount of MES powder: Determine the desired volume and concentration of the MES buffer. Calculate the amount of MES powder needed using the formula: Amount of MES powder (g) = Concentration (M) x Volume (L) x Molecular weight of MES (195.24 g/mol).
- Dissolve MES powder in water: Add the calculated amount of MES powder to a beaker containing a small volume of deionized water. Stir the solution using a magnetic stirrer until the powder dissolves completely.
- Adjust the volume: Gradually add more deionized water to the solution while stirring until the desired volume is reached.
- Adjust the pH: Use a pH meter to measure the pH of the solution. Adjust the pH to the desired value (typically 6.1) by adding small amounts of 1 M NaOH or 1 M HCl as needed.
- Filter the solution: If necessary, filter the solution to remove any impurities or precipitates.
Variations and Modifications
The basic MES buffer preparation method can be modified to suit specific applications or requirements. Here are some common variations:
- Buffer concentration: The concentration of the MES buffer can be adjusted to suit the experimental needs. Common concentrations range from 0.01 M to 1 M.
- pH adjustment: The pH of the MES buffer can be adjusted to different values depending on the application. It is commonly used in the pH range of 5.5 to 6.5.
- Additives: Additional components, such as salts or detergents, can be added to the MES buffer to enhance its stability or functionality in certain applications.
Properties and Characteristics
Mes buffer exhibits several unique physical and chemical properties that contribute to its effectiveness and stability in various applications.
Physically, mes buffer appears as a colorless, odorless liquid with a pH value between 5.5 and 6.7. It is highly soluble in water and can form stable solutions across a wide range of concentrations.
Chemically, mes buffer is a zwitterionic compound, meaning it contains both positive and negative charges within its molecular structure. This unique property allows it to effectively buffer solutions against changes in pH, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring precise pH control.
pH Stability
One of the most important characteristics of mes buffer is its exceptional pH stability. The pKa of mes buffer is approximately 6.1, indicating that it is most effective at buffering solutions within a pH range of 5.5 to 6.7. Within this range, mes buffer exhibits a high buffering capacity, meaning it can effectively resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
Temperature Dependence
The effectiveness of mes buffer is also influenced by temperature. As temperature increases, the pKa of mes buffer decreases slightly, resulting in a reduction in its buffering capacity. This means that mes buffer may not be as effective at maintaining pH stability in solutions exposed to high temperatures.
Other Factors
In addition to pH and temperature, other factors can also affect the stability and effectiveness of mes buffer. These include the presence of ions, solvents, and other chemicals in the solution. The presence of certain ions, such as calcium or magnesium, can interact with mes buffer and alter its buffering capacity.
Similarly, the choice of solvent can also impact the solubility and effectiveness of mes buffer.
Applications in Research
Mes buffer finds widespread use in scientific research across various fields, owing to its ability to maintain optimal conditions for biological processes.
In biochemical studies , mes buffer is employed to control pH and ionic strength during enzyme assays and protein purification procedures. Its buffering capacity ensures that the pH remains stable, preventing denaturation or inactivation of enzymes and proteins.
Cellular and Molecular Biology
In cellular and molecular biology , mes buffer is used in cell culture media to maintain pH and osmotic balance. It facilitates optimal growth and viability of cells by providing a stable environment for cellular processes.
Troubleshooting and Optimization
Mes buffer preparation is generally straightforward, but certain issues can arise during the process. Understanding common problems and employing troubleshooting methods can help optimize the buffer’s performance and ensure accurate experimental results.
Below are some common issues and suggested solutions to help troubleshoot and optimize Mes buffer preparation:
Incorrect pH Measurement
- Issue: The pH measurement is inaccurate or unstable.
- Solution: Calibrate the pH meter using standard pH buffers before use. Ensure the electrode is clean and properly immersed in the buffer solution.
Buffer Instability
- Issue: The buffer solution becomes cloudy or precipitates over time.
- Solution: Use high-quality reagents and store the buffer at the appropriate temperature (usually 4°C). Avoid contamination by using sterile technique and materials.
Insufficient Buffer Capacity
- Issue: The buffer cannot maintain the desired pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
- Solution: Increase the concentration of the buffer components (MES and Tris) or add a stronger buffer with a higher pKa value.
Contamination
- Issue: The buffer solution shows signs of contamination, such as bacterial growth or discoloration.
- Solution: Use sterile technique and materials during preparation. Store the buffer in a clean and sealed container to prevent contamination.
Safety Considerations
Mes buffer is generally considered safe to handle, but it’s important to be aware of potential hazards associated with its components and follow proper safety practices.
Mes (2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid) is a mild irritant and may cause skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritation upon contact or inhalation. It is recommended to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, eye protection, and a dust mask, when handling Mes powder.
Safe Storage
- Store Mes powder in a cool, dry place away from heat and light.
- Keep the container tightly sealed to prevent moisture absorption.
Safe Disposal
- Dispose of unused Mes solution and contaminated materials according to local regulations for chemical waste.
- Neutralize the solution before disposal by adding an appropriate base, such as sodium hydroxide.
Safe Handling
- Avoid direct contact with Mes powder or concentrated solutions.
- Handle Mes in a well-ventilated area.
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling Mes.
Alternatives and Comparisons
MES buffer is a versatile and widely used buffer system, but there are other alternatives available that may be more suitable for specific applications. Each buffer system has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which buffer to use depends on the specific requirements of the experiment.
Phosphate Buffer
Phosphate buffer is another commonly used buffer system that is composed of a mixture of phosphoric acid and its conjugate base, sodium phosphate. Phosphate buffer is often used in biological applications because it can maintain a stable pH over a wide range of temperatures and ionic strengths.
However, phosphate buffer can interfere with some enzymatic reactions, and it can also form precipitates with calcium and magnesium ions.
Tris Buffer
Tris buffer is a buffer system that is composed of a mixture of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris) and its conjugate acid, hydrochloric acid. Tris buffer is often used in molecular biology applications because it is non-toxic and does not interfere with most enzymatic reactions.
However, Tris buffer has a relatively low buffering capacity and can be unstable at high temperatures.
HEPES Buffer
HEPES buffer is a buffer system that is composed of a mixture of 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) and its conjugate base, sodium hydroxide. HEPES buffer is often used in cell culture applications because it is non-toxic and has a high buffering capacity.
However, HEPES buffer can be expensive and can interfere with some enzymatic reactions.
Last Point
In conclusion, mes buffer recipe is a fundamental aspect of scientific research, providing a reliable and versatile means of maintaining optimal conditions for biological processes. By understanding the principles behind mes buffer preparation, researchers can harness its potential to advance their investigations and contribute to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
We encourage readers to explore the resources and information provided in this guide to enhance their understanding and proficiency in working with mes buffer.
Q&A
What is the purpose of mes buffer?
Mes buffer is primarily used to maintain a specific pH in a solution, typically within the physiological range. It is particularly useful in biological applications where precise pH control is essential for enzyme activity, protein stability, and other biochemical processes.
What are the advantages of using mes buffer?
Mes buffer offers several advantages, including its high buffering capacity, stability over a wide pH range, and low toxicity to biological systems. Additionally, mes buffer is relatively easy to prepare and can be used in a variety of applications.
What are the potential hazards associated with mes buffer?
Mes buffer components, such as MES (2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid), can be irritants to the skin and eyes. Proper handling, storage, and disposal practices are essential to minimize potential hazards.
